Open Schooling
Open Schooling: Info, Eligibility, Fees, Top 10 Open Schools, Admission
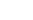 DURATION :
DURATION :
1 Year
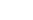 FEES :
FEES :
10000 – 30000 INR Per Year
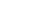 ELIGIBILTY :
ELIGIBILTY :
10th - 14+ Age & Literate
12th - 16+ Age & 10th Pass
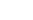 BOARDS :
BOARDS :
10+ Boards are Offering Open School Education
Get In Touch
About Open Schooling
Open schooling, as the name suggests, presents an unconventional approach to school education in India, allowing students the opportunity to pursue Secondary (10th) & Senior Secondary (12th) courses that are equivalent to those offered in conventional schools. It is integrated into the Indian education system as a recognized and alternative form of education, alongside traditional schooling, to serve the different needs of students who may not be able to attend regular schools. It offers a flexible approach to learning which is ‘open’ in terms of timing, location, teaching roles, methods, access, and other related factors. This openness helps the learners to go with their additional commitments which can be related to family or work responsibilities.
Open schooling involves distance and online learning techniques, allowing students to learn at their own pace and convenience, using self-learning materials, online resources, and occasional in-person support. This method of schooling is beneficial for individuals who are unable to engage in formal schooling and for those who missed opportunities to complete their schooling due to various reasons such as job commitments, financial issues, health issues, and other personal circumstances. It is also a blessing for mentally or physically challenged individuals, homemakers, school dropouts, and young individuals forging their own career path. Open Schooling is designed to impart high school education to learners, regardless of their age, location, or specific needs.
The Emergence of Open Schooling in India
The concept of open schooling in India started in November 1989 with the establishment of National Open School (NOS) by the Government of India. Its primary goal was to provide education to a wider and more diverse population, especially those who were unable to access traditional formal school education for various reasons. The National Open School (NOS) originated from the CBSE-sponsored open school project initiated in 1979. In 2002, it was renamed as the National Institute of Open Schooling (NIOS).
NIOS is a national level open schooling board of education in India, governed and managed by the Central Government of India. National Institute of Open Schooling (NIOS) conducts the secondary and senior secondary examinations of the open school system, which are considered equivalent to the CBSE & ICSE Exams held in India. NIOS is the largest open schooling board in the world that enrolls more than 3.5 lakhs students annually for various courses conducted by it. Apart from NIOS, in India, there are other State Open Schooling Boards such as the Board of Open Schooling and Skill Education (BOSSE), Bihar Board of Open Schooling and Examination (BBOSE), and Delhi State Open School (DSOS) also offering open schooling programs.
Who regulates Open Schooling in India?
In India, education is governed by different levels of government. The central government, led by the Ministry of Education, plays a crucial role in making and overseeing education policies. On the other hand, each state government has its own education department, responsible for managing school education in that state.
These departments establish education boards at the national and state levels to make education more accessible across different regions. There are two main types of education boards: Central Boards, which are established and governed by the national government, and State Boards, which are set up and regulated by individual state governments.
In the traditional approach to education in India, students usually attend schools affiliated with central or state education boards such as the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) and various State Boards. These conventional education boards are responsible for setting curriculum standards, conducting examinations, and granting certificates for various educational levels. These boards receive recognition and oversight from the respective central or state government authorities.
On the other hand, open schools like the National Institute of Open Schooling (NIOS) offer an alternative educational system. Open schools also receive recognition and regulation from the same government authorities, either at the central or state level. For instance, NIOS is acknowledged by the Central Government of India and BOSSE is recognized by the Sikkim State Government. Although open schools employ different instructional methods, they offer qualifications equivalent to those offered by traditional education boards. Both traditional and open boards are recognized by either state or central education authorities, ensuring the quality and standards of education in India.
Acceptance Of Open Schooling Boards
The acceptance of open schooling certificates is not limited to a particular sector. They have found their way into the mainstream of the Indian education system. Universities and colleges, both in India and abroad, acknowledge the merit of open schooling qualifications, opening doors for further studies in diverse fields.
Employers across various industries in India recognize the value of these certificates. They view open schooling as well-prepared and capable individuals, ready to contribute to the workforce. This level of acceptance has increased the employability of those who have chosen open schooling as their educational path.
Also, the Indian government's support for open schooling initiatives has played a pivotal role in fostering this acceptance. It aligns with the larger objectives of education reform and the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, which emphasizes alternative education pathways, including open schooling, as a means to expand access to education and skill development.
Hence, in simple words, we can understand that:
- Open schooling certificates are recognized and accepted by schools of all types, making them a suitable choice for students who want to pursue higher education.
- Private companies highly value open schooling certificates, seeing them as proof of an individual's skills and determination.
- Open schooling certificates are acknowledged and embraced by both central and state government sectors.
So, the acceptance of certificates from open schooling boards in India has grown significantly, making them a respected and practical choice for students seeking quality education and a pathway to diverse opportunities in India and across the world.
Valid boards in India
In India, there are several valid education boards, both at the central and state levels, established and recognized by the government through executive orders. Whether it's a regular or open school, these educational boards are acknowledged and endorsed by either the state or central governments only.
These boards play a crucial role in conducting examinations and certifying students' educational qualifications.
You can check the list of valid boards in India through the “Council of Boards of School Education” (COBSE), an organization that maintains a list of valid boards in the country.
To check the list of valid boards in India, one can go to the website of COBSE: https://www.cobse.in
Difference between regular and open schooling
Open schooling in India and regular schooling have some key differences:
| Open Schooling | Regular Schooling | |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility and Personalization |
|
|
| Subject Selection and Compulsory Subjects |
|
|
| Teaching Methods and Learning Environment | Self-instructional materials (videos, audio, textbooks) | Access to physical facilities (libraries, labs, sports) |
| Assessment and Examinations |
|
|
Flexibility and Customization
- Open schooling allows students to learn at their own pace, on their own schedule, and using different methods.
- It's great for those who want to study while pursuing other interests or were unable to complete their schooling before.
- Regular schooling follows a strict timetable and focuses on student-teacher interaction.
Flexibility and Customization
- In regular schools, students must study all subjects, including
languages, science, math, and social studies.
- Open schooling lets students choose 5 to 7 subjects.
- They can even change subjects during their studies.
- Students can pick from three languages for instruction, and only one
language is compulsory.
- They can also choose vocational subjects.
Teaching Methods and Learning Environment:
- Open schooling uses self-instructional materials like videos, audio,
or textbooks.
- Regular schools offer facilities like libraries and labs, providing
hands-on learning opportunities.
Assessment and Examinations
- Regular school students must meet strict attendance rules to
pass exams.
- Open school students can complete their 10th and 12th grades
through boards like NIOS, BOSSE, and others.
- Students can transfer credits and choose their own pace of
learning.
Teaching Methods and Learning Environment:
- Open schooling uses self-instructional materials like videos, audio, or textbooks.
- Regular schools offer facilities like libraries and labs, providing hands-on learning opportunities.
Assessment and Examinations
- Regular school students must meet strict attendance rules to
pass exams.
- Open school students can complete their 10th and 12th grades
through boards like NIOS, BOSSE, and others.
- Students can transfer credits and choose their own pace of
learning.
Advantages of Open schooling
Open schooling offers self-learning options that cater to students' schedules, teaching methods, locations, and ways of access. This allows students to learn at their own pace, which is particularly beneficial for those who wish to continue their studies. Education becomes accessible to everyone at any time and anywhere through open schooling.
- Education for all: Open schooling ensures that all students, regardless of their abilities or socio-economic status, have access to school education. It promotes equal access for everyone, regardless of their race or gender, making education more accessible.
- Diverse Opportunities: Many people think that if you study with NIOS or other state Boards, you won't be able to go to good colleges. But you'll be surprised to know that many have made it to top institutions like IITs, Delhi University, Punjab University, and more. Students who pass NIOS exams or from other boards can get into medical and engineering colleges, and they can even take competitive exams like IIT-JEE, AIEEE, NEET, and other professional and academic courses at universities in India and abroad. They can also apply for government jobs at both central and state government levels. So, NIOS or other State Boards for open schooling can open doors to a bright future.
- Affordable Education: Open schooling is a cost-effective choice compared to traditional education. It eliminates the need for new school buildings, fancy equipment, and associated infrastructure costs. Students can study comfortably from the convenience of their homes, which not only reduces expenses but also makes education more budget-friendly. This affordability widens the opportunity for quality education to those who might not afford traditional schooling.
- No Age Limit: Open schooling doesn't have an age limit. This means anyone of any age can go back to school and finish their 10th and 12th grade. This is particularly beneficial for adults who may have had to discontinue their education for various reasons. The absence of an age limit encourages lifelong learning, ensuring that individuals of all ages can access educational opportunities.
- Transfer of credit: The flexibility of transferring up to two subjects from national, state boards, or state open schools offers students the choice to personalize their learning journey. This is advantageous for those who have previously completed some subjects and want to build upon that knowledge at their own pace. The option to transfer credits from various boards adds another layer of flexibility to the educational experience, allowing students to tailor their curriculum to their specific needs and interests.
Courses offered under Open Schooling
State and central boards under open schooling offer a wide range of courses and programs to cater to the diverse educational needs of students.
Open schooling boards primarily emphasize on 10th and 12th-grade education, providing flexible and accessible options for students to complete their 10th and 12th-grade studies.
These programs are designed to provide flexible learning options and to accommodate various academic and vocational interests. Here are some common courses and programs offered:
Secondary (10th Grade) Programs:
- Secondary School Examination (10th standard) is the foundational program offered by open schooling boards.
- Core subjects include Mathematics, Science, Social Science, and Languages (e.g., English, Hindi, regional languages).
- Elective subjects are often available, allowing students to explore specific interests or skills.
Senior Secondary (12th Grade) Programs:
- Senior Secondary programs are the next level of education provided by open schooling boards.
- Core subjects include Physics, Chemistry, Biology, Mathematics, Business Studies, Economics, Accountancy, and Languages.
- Elective subjects can vary by board and may include subjects like Computer Science, Political Science, Sociology, and more.
Vocational and Skill Development Programs:
- Many open schooling boards offer vocational and skill development courses that prepare students for specific careers or industries.
- These programs cover a wide range of fields, such as healthcare, information technology, agriculture, tourism, and more.
- Certification in various skills, trades, and vocations is often available.
Open Basic Education Programs:
- Some open schooling boards provide basic education programs for individuals who may have missed out on early education.
- These programs typically cover basic literacy and numeracy skills and may lead to a certification equivalent to 3rd, 5th, or 8th standard.
Life Enrichment programs
- These are non-formal courses focused on personal development and life skills enhancement. They cover a variety of topics, including art, music, yoga, and other skills that enrich one's life.
Diploma in Elementary Education (D.EL.ED.) Course
- This program is intended for individuals aspiring to become teachers. It provides the essential training and qualifications required for teaching at the elementary education level.
Courses for ITI Students
- These specialized secondary and senior secondary courses are tailored to the specific needs of students who have completed programs at Industrial Training Institutes (ITIs) and wish to further their education.
Open Schooling Eligibility
The eligibility criteria for admission in open schooling vary upon the program the student wants to choose (secondary and senior secondary program). Let’s understand the criteria according to the program:
- One needs to be at least 14 years old.
- One must know how to read and write.
- To be eligible for open schooling in 12th standard in India:
- One needs to be at least 16 years old.
- One must have completed your 10th grade.
- There should be a gap of at least one year between their 10th and 12th grade.
To be eligible for open schooling in 10th standard in India:
Open Schooling Fees
The fees for open school education in India can differ based on the specific open schooling board and the chosen course. Here are some examples of fee structures for open school boards in India:
National Institute of Open Schooling (NIOS): The fee structure varies for class 10th and class 12th. For class 10th, the fee is Rs. 480 per subject, while for class 12th, it's Rs. 500 per subject for theory, with an additional Rs. 200 for practical per subject. If a student enrolls in 5 subjects for class 10th, the total fees amount to Rs. 1800, and for class 12th, it totals Rs. 2000. Opting for an additional subject in both classes incurs a fee of Rs. 720. These fees reflect the cost structure for pursuing education through NIOS at these grade levels.
Board of Open Schooling and Skill Education (BOSSE): The fee structure is flexible and depends on the course chosen. To register with BOSSE, there is a basic registration fee of Rs. 500. The fees for secondary and senior secondary courses are Rs. 1200 and Rs. 1300, respectively. Additionally, if students opt to take an extra subject in both secondary and senior secondary classes, they are required to pay a fee of Rs. 720. This fee arrangement accommodates a range of courses and academic choices offered by BOSSE.
Likewise, the fees for other open school boards in India may differ based on the specific board and the chosen course. To get the most up-to-date fee structure, it's a good idea to check the official website of the specific board in which you are interested.
Examination blocks and duration in Open Schooling
The duration of open schooling programs can differ depending on the examination blocks provided by various educational boards. Some boards offer two examination blocks, while others offer three.
For example, Board of Open Schooling and Skill Education (BOSSE) offers two examination blocks, scheduled in April and October. On the other hand, National Institute of Open Schooling (NIOS) provides four distinct streams, which include two blocks, Transfer of Credits (TOC) and On-demand Examination (ODE).
The last dates for these examination blocks are determined and provided by the respective boards. This allows students to select a schedule that best suits their individual learning speed and preferences, providing them with the flexibility needed to complete their coursework and assessments at their own pace.
Open Schooling Syllabus
The syllabus of an open schooling program may vary depending on the specific open schooling board or institution that students choose for their education. Open schooling boards, such as NIOS, offer a range of courses in either secondary (10th) or senior secondary programs (12th).
Students must visit the official website of the open schooling board or institution to get the detailed information and available subjects in the respective program they are looking for. Here is the general layout of the curriculum provided for secondary and senior secondary programs:
- Core subjects: For the specific program, certain core subjects are mandatory to be selected. For the secondary program, these core subjects include mathematics, science, social science, English, and a regional language.
- Elective subjects: Students have the freedom to choose subjects from a list based on their interests for the particular program. For instance, in the senior secondary program, students can select elective subjects that align with their preferences, such as choosing between options like Biology, Mathematics, Zoology, and more in the science stream.
- Practical subjects: There are practical examinations or projects depending on the program or the course that students opt for.
- Additional Subjects: Students have an option to include an additional subject in their program which varies from their core subjects. For the secondary program, students can add additional subjects such as IT or any language subject.
To get more detailed and accurate information regarding the subjects according to the program, students visit the official website of the open schooling board or institution they are interested in. There students would get the course information, syllabus, ebooks and exam pattern.
The syllabus in open schooling is similar to that of regular schools, covering core subjects such as Mathematics, Science, Social Science, and Languages. However, open schooling provides students with the freedom to choose subjects, even from different academic streams, aligning with their individual interests.
Open Schooling Admission process
Getting into open schooling for 10th and 12th in India is a step-by-step process. Remember, the admission process can vary between different open school boards. The admission process can be done online by visiting the official website of the open schooling board or can also visit the office or at the study centers of the board in person.
The admission process can vary from board to board like NIOS, BOSSE, etc. The below mentioned is a general procedure for admission:
- Visit the official website or office/study center of the open schooling institution: Here the student will get the details of the institution and also the application form for processing the admission.
- Download and fill the application form: Go through the form and fill out the complete application form in an accurate manner. Attach the required documents needed to complete the admission process.
- Submission of form: After filling the form and attaching the documents, submit the form in person or mail to the office of the open schooling institution or study center or online.
- Verification: Your application form along with the documents will be verified by the institution to confirm whether the student sits in the eligibility criteria.
- Fees payment: Pay the prescribed fees of the program to the institution as per the guidelines of the respective board.
- Confirmation: After completing the above-mentioned process and payment of fees, students will receive a confirmation regarding their admission in the applied program by the open schooling institution.
Documents required for Open Schooling
For 10th-grade:
- Passport size photo of the student
- Identity proof (Aadhar Card)
For 12th-grade:
- Passport size photo of the student
- Identity proof (Aadhar Card)
- 10th marksheet
FAQs
Yes, open schooling is recognized by traditional educational institutions, and students can pursue higher education at universities and colleges after completing open school programs.
Absolutely! Open Schooling opens doors to top universities, both in India and abroad. Students can appear for competitive exams and pursue a wide range of courses.
Compared to traditional schooling, Open Schooling is a budget-friendly option. It eliminates the need for new infrastructure, making education more economical.
No, Open Schooling welcomes students of all ages. There are no age restrictions, allowing individuals to resume their education at any stage of life.
Yes, students have the option to transfer credits from recognized national, state boards, or state open schools. They can transfer for two subjects.
Indeed, certificates from Open Schooling boards hold recognition by many employers, schools, universities, and colleges. They are considered equivalent to traditional certificates.
Open schooling boards offer a variety of support services to students, including:
- Online tutoring
- Discussion forums
- Academic advising
- Career counseling
- Library service
Open schooling in India is typically government-regulated and can be both government-funded and operated by government boards. There are also some private institutions that offer open schooling programs, but valid open schools are governed and regulated by either the Central or State government.
Yes, you can generally apply for professional courses with an open schooling certificate, but it's essential to verify the specific eligibility requirements of the professional course or institution you wish to apply to, as they may have certain admission criterias.











